Added support for configurable CLI settings that can be managed via yepcode settings:get, yepcode settings:set, and yepcode settings:remove commands. The following settings are now available
disableUpdateNotifier (default: `false`) - Disable update notifierignoreProcessVersions (default: `false`) - Ignore process versions so they are not downloaded on clone or pullignoreWorkspaceNotEmpty (default: `false`) - Ignore workspace not empty errorignoreYepCodeRunProcesses (default: `false`) - Ignore YepCode run processes so they are not downloaded on clone or pulllocalVariablesFileName (default: `variables.local.env`) - Local variables file nameskipAiAssitantSetup (default: `false`) - Skip AI assistant setupvariablesFileName (default: `variables.env`) - Variables file nameOur one-line pitch has always been “The Zapier for Developers” — but maybe it’s time for a new one: “The Lovable for Automations” 🤔
After building in stealth mode, we’re excited to unveil Yep Agent: an AI coding partner designed for the modern integration landscape.
Yep Agent can:
Just talk — Yep Agent listens, codes, connects, and delivers. Fast, adaptive, and fully in your control.
To complement the new AI agent rules included in YepCode CLI clone, we’ve added the ability to automatically generate API credentials for accessing the YepCode MCP Server directly from local AI coding agents.
For each supported agent, we set up the proper MCP configuration, so the agent can securely and seamlessly interact with YepCode API and processes. This allows AI agents to call any MCP method or API endpoint directly from a prompt, taking full advantage of YepCode’s capabilities without manual configuration.
We’ve added support to the YepCode CLI clone command to generate clear, structured rules that can be consumed by AI coding agents. These rules are also available in our docs platform help agents better understand YepCode projects and how to work with them.
Currently supported agents:
While YepCode projects remain fully portable and avoid vendor lock-in, these rules allow AI agents to take advantage of YepCode’s built-in capabilities out of the box—such as parameters, datastore, and storage—resulting in more accurate and productive code generation.
Endpoint: https://cloud.yepcode.io/mcp/{teamSlugOrApiKey}
We’ve added support for streamable connections to the MCP server — allowing clients to open continuous HTTP streams and receive real-time updates without polling.
Highlights:
teamSlugapiKeyURL examples:
https://cloud.yepcode.io/mcp/my-teamhttps://cloud.yepcode.io/mcp/sk-abc123xyzIn our MCP server, we’ve replaced the disableRunCodeTooltools
You can now define which tools are enabled by using a comma-separated list of built-in tool categories and process tags:
run_codeexecutionsenv_varsstoragemcp-toolcoreapiautomationIf no tools are specified, all built-in tools are enabled by default, but no process tools are exposed.
Example SSE URL definition:
https://cloud.yepcode.io/mcp/sk-c2E....RD/sse?mcpOptions=runCodeCleanup&tools=run_code,storage,env_vars,core,api
We’ve upgraded our execution engine to Firecracker version 13, bringing significant improvements in performance, security, and efficiency. This upgrade enhances isolation between executions, reduces startup latency, and improves resource utilization — making your processes faster and more reliable. Firecracker 13 also includes the latest security patches and optimizations, ensuring a safer and smoother execution environment.
At YepCode, we prioritize keeping our execution engine and dependencies up to date. This upgrade is part of our ongoing commitment to maintain cutting-edge performance and security for all users.
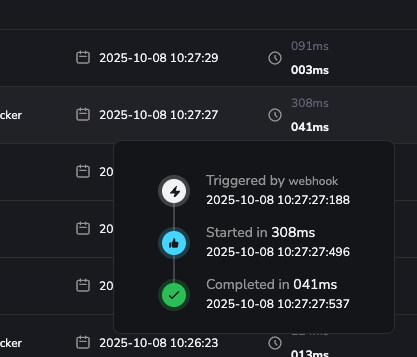
We’ve enhanced the execution row display to include both the startup delay (the time it took for the execution to begin) and the total duration. These two metrics are now shown together in the same cell for easier comparison. Additionally, hovering over the cell reveals the full execution timeline for more detailed insights.
We’ve upgraded our runtime environments to Node.js 22.19 and Python 3.13.7, bringing improved performance, stability, and access to the latest language features.
At YepCode, we always keep our runtimes up to date so you can rely on a secure, efficient, and future-proof execution platform.